[Path Planning] Performance Optimization Using Quadtree Structure
This post is written by YoungJ-Baek
1. What is Quadtree
Our kind neighbor, Wikipedia introduces Quadtree as followed.
A quadtree is a tree data structure in which each internal node has exactly four children. Quadtrees are the two-dimensional analog of octrees and are most often used to partition a two-dimensional space by recursively subdividing it into four quadrants or regions.
2. The example of Quadtree
We focus on this point. Quadtree is used to partition a two-dimensional space by recursively subdividing it into four regions. It uses four children. The concept image of quadtree is as followed.
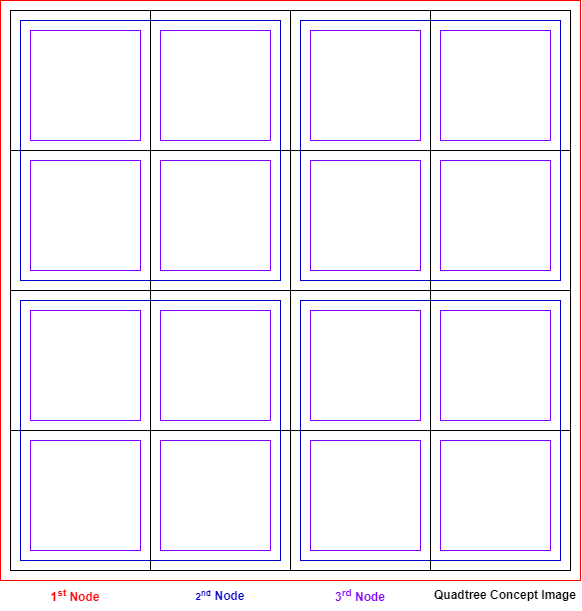
Since this data structure can search the target with big steps, we can find the shortest path with less computational cost. Also, we can make the grid map easily via gathering pixels that have same value. In this case, 0 or 1 can be the value.
For example, quadtree can compress the image below in a simple way. You can find the more details about quadtree example in this great blog.
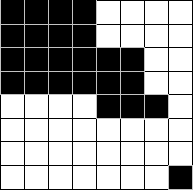
The result for the compression becomes this, (0(1101)1((0011)(0111)1(1110)).
Moreover, you can find the real usage of quadtree as followed with the real image. If you are interesting at Image Processing, you might be familiar with the image. You can find more details about this implementation in here.
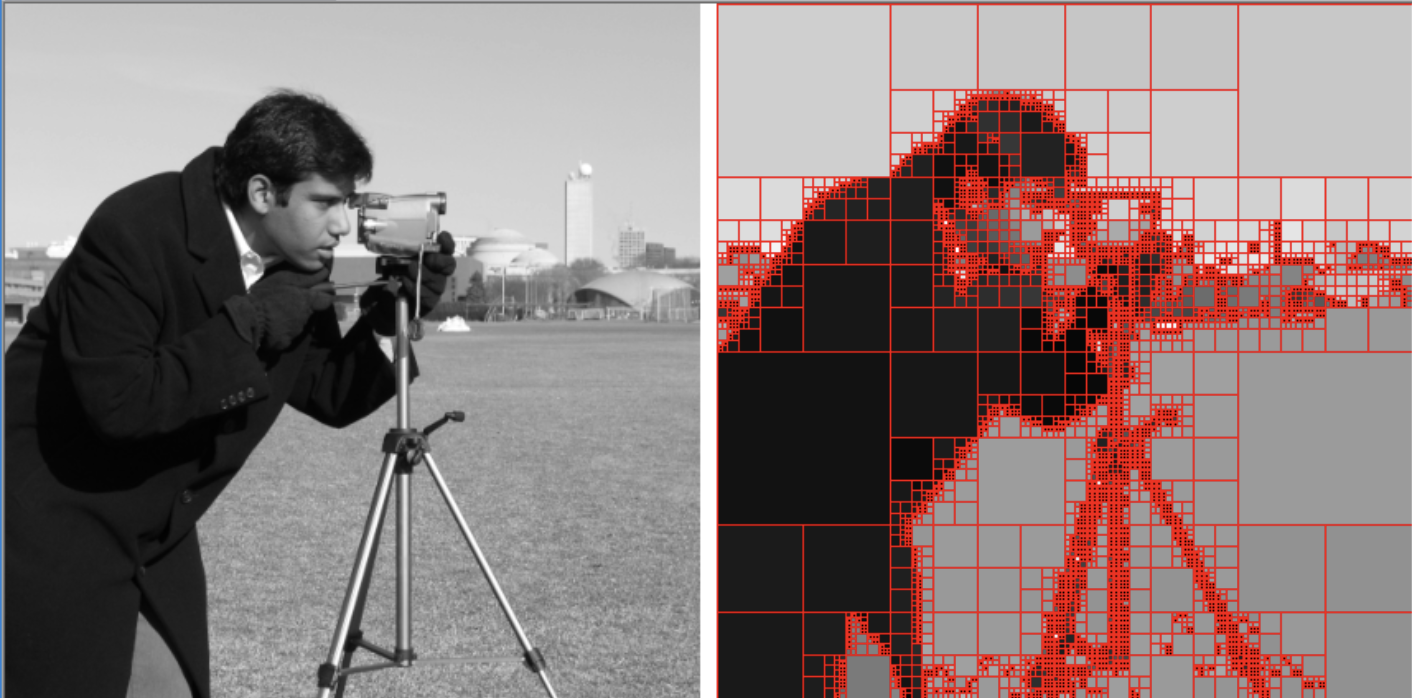

3. Conclusion
By the way, we can make the 2D grid map much faster and less computation via quadtree. As a result, we can find the shortest path via using A* path finding algorithm and quadtree data structure. Thanks to the amazing project by Volker Poplaswki, we can reduce the time cost for the experiment. The image below is an example of quadtree grid map with KITTI dataset (sequence 00).

In a conclusion, we modularized the process, from the PCD map to the shortest path. In the process, we convert the PCD map into 2D grid map using quadtree, and find the shortest path with A* algorithm. Our next step for the path planning is to modify the code to be able to set up start and end point with arguments or parameters (currently using configuration file). Then, we are planning to optimize the source code via Python to C++ conversion. Also, we are going to test other algorithms and data structures for better performance, but it would be our optional to-do list since the combination of quadtree + A* algorithm already shows high performance and reliability. It takes about 1 or 2 seconds to find the shortest path with KITTI map.
Our result is uploaded in the repository.

Leave a comment